Management of Chemical Substances
Basic Approach
Based on laws and regulations such as the Act on Confirmation, etc. of Release Amounts of Specific Chemical Substances in the Environment and Promotion of Improvements to the Management Thereof (Pollutant Release and Transfer Register Act), the ENEOS Group strives to properly manage chemical substances and reduce emissions of such substances. In addition, we are shifting to chemicals with lower impacts on health and the environment.
We are also committed to properly managing chemical substances not covered by these laws and regulations.
Structure
For information on our structure, see Environmental Management.
Major Initiatives
Compliance with Laws and Regulations
Management and Monitoring of Specified Chemical Substances under Japan’s Pollutant Release and Transfer Register Act
The Group manages and monitors the release and transfer amounts of specified chemical substances, such as benzene, toluene, and xylene, which are found in gasoline, based on Japan’s Pollutant Release and Transfer Register Act.
In fiscal 2024, the Group’s releases totaled 2,337 tonnes, a decrease of 157 tonnes over the previous fiscal year, and transfers totaled 1,096 tonnes, an increase of 421 tonnes over the previous fiscal year. The increase in transfers from the previous year is due to revisions in the scope of aggregation.
- For information about , see the Editorial Policy.
Release of Specified Chemical Substances
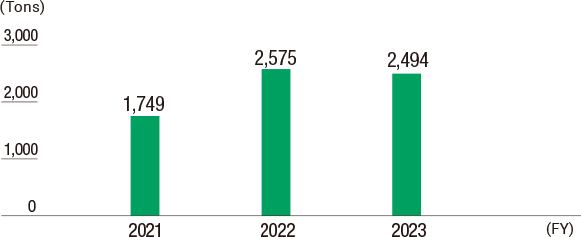
Transfer of Specified Chemical Substances
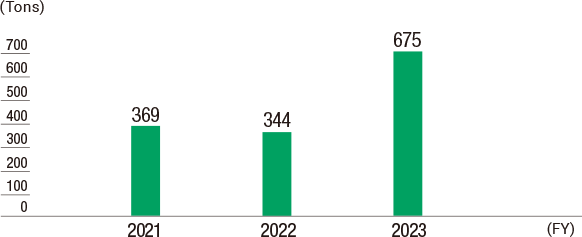
- Note:For detailed data, see Data.
Management of PCB* Waste
The Group carries out storage notification and systematic treatment of PCB waste based on Japan’s Act on Special Measures concerning Promotion of Proper Treatment of PCB Wastes (PCB Special Measures Act).
- *Polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB): Due to its excellent electric insulation properties, this chemical compound was used mainly in applications such as insulating fluids for transformers and capacitors, and carbonless copiers. However, its production and import are now prohibited.
Compliance with Domestic and International Regulations
Laws and regulations on the handling of chemical substances are being developed both in Japan and abroad to protect the environment, as well as safety and health. There are also cases where countries have newly implemented chemical substance registration systems or modified existing ones.
The Group takes necessary measures, such as registering substances in chemical substance registration systems in accordance with regulations in Japan and abroad, including the REACH Regulation in Europe and the Act on the Regulation of Manufacture and Evaluation of Chemical Substances in Japan.
Guidelines on Chemical Substances in Our Products and Management of Chemical Substances
ENEOS has voluntarily established standards for managing the chemical substances used in its products. We have specified prohibited substances (such as most organochlorine compounds, mercury compounds, lead compounds, and phthalates) and substances that require monitoring (such as VOCs including toluene and xylene) to better manage their use in products, and we are working to mitigate any harmful effects they may have.
In addition, at ENEOS and ENEOS Materials, we provide essential product safety information to customers and others involved with our products using methods such as safety data sheets (SDS). In the event that we obtain new information about any hazards or environmental impacts of our products, we promptly update the relevant SDS to provide the latest information to customers and all parties involved with our products.