Prevention of Global Warming
Basic Approach
The ENEOS Group is reducing CO2 emissions across the entire supply chain in order to achieve a decarbonized, circulating society.
To reduce operational greenhouse gas emissions, we are focusing on energy conservation in our business activities. We are also helping to reduce downstream greenhouse gas emissions from sold products through the expansion of our renewable energy business, utilization of biomass and other resources as well as hydrogen and synthetic fuels, and development and sales of environmentally friendly products that have a lower environmental impact.
For our Group-wide initiatives to address climate change and TCFD-related information, see Our Response to Climate Change Risks and Opportunities (TCFD).
Structure
For information on our structure, see Environmental Management.
In May 2024, we established the Carbon Neutrality Promotion Committee, chaired by the CTO, to promote carbon neutrality across the Group. The committee updates the basic strategies in response to the business environment, while each operating company formulates specific action plans based on these basic strategies.
In fiscal 2024, the committee primarily discussed the Carbon Neutrality Plan 2025 edition, which will serve as a guideline for the Group's efforts to achieve a carbon-neutral, circulating society. During the discussions, we identified key drivers with a high degree of uncertainty that will impact our greenhouse gas emissions reduction pathways and presumed multiple societal scenarios. We will continue to hold management-level discussions on our carbon neutrality strategy and will work with the government and society to promote efforts to achieve a carbon-neutral, circulating society.
Material Issues, Plans and Results
Fiscal 2024 Targets, Results and Progress
Evaluation: Achieved/Steady progress Not achieved
| Material ESG Issue | Initiative | Target (KPI) | Results/Progress | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contribution to the development of a decarbonized society | Reduction in CO2 emissions | Reduction in CO2 emissions: Reduce emissions to 29.50 million tonnes or less | 24.68 million tonnes | |
Results
- For information about , see the Editorial Policy.
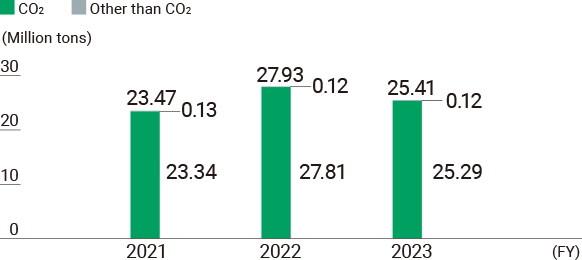
Changes in Total Greenhouse Gas Emissions (Scope 1+2)
- Notes:
- Calculated in accordance with the Act on Promotion of Global Warming Countermeasures, taking into account electricity sold and heat sold.
- For detailed data, see Data.
- The Group’s greenhouse gas emissions (Scope 1 and 2) are calculated using the controlled approach in the GHG Protocol and cover main applicable organizations.
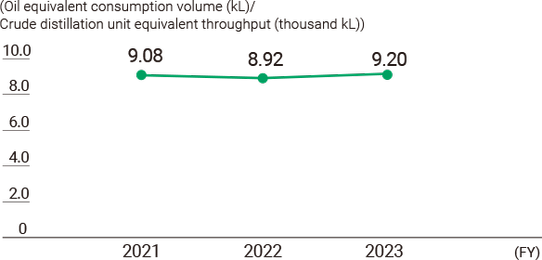
Energy Consumption Intensity for Oil Refining
- Note:
- Covers the oil refining sites of the ENEOS Group.
Breakdown of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Other Than CO2 (Fiscal 2024)
| Items | Unit | Emissions |
|---|---|---|
| Total GHG emissions other than CO2 | Tonnes | 135,841 |
(1)CH4 (methane) |
Tonnes | 39,131 |
(2)N2O (nitrous oxide) |
Tonnes | 95,986 |
(3)HFCs (hydrofluorocarbons) |
Tonnes | 328 |
(4)PFCs (perfluorinated compounds) |
Tonnes | 0 |
(5)SF6 (sulfur hexafluoride) |
Tonnes | 396 |
(6)NF3 (nitrogen trifluoride) |
Tonnes | 0 |
The main greenhouse gases other than CO2 are CH4, produced during crude oil and gas production, and N2O, which is emitted from heating furnaces during the oil refining process.
We will continue working to lower these and other greenhouse gas emissions.
Carbon Neutrality Plan
Target
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Results (Scope 1+2)
| Applicable companies | Items | Unit | FY2023 results | FY2024 results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENEOS | GHG emissions | Million tonnes | 23.98 | 21.28 |
| Reduction in emissions from refineries, etc. | Million tonnes | -0.57 | -0.68 | |
| CCS | Selection of potential storage sites | Determination of storage sites | ||
| Credits created through removal by forests* | Cumulative total of 0.23 million tonnes created | Cumulative total of 0.30 million tonnes created | ||
| ENEOS Xplora | GHG emissions | Million tonnes | 0.71 | 0.85 |
| Methane emissions | Tonnes | 802 | 1,126 | |
| CCUS | Million tonnes | 0.25 | 0.68 | |
| JX Advanced Metals | GHG emissions | Million tonnes | 0.72 | 0.60 |
| ENEOS Materials | GHG emissions | Million tonnes | - | 0.96 |
| ENEOS Power | GHG emissions | Million tonnes | - | 0.98 |
| ENEOS Renewable Energy | GHG emissions | Million tonnes | - | 0 |
| Group total (Results compared to FY2013) |
GHG emissions | Million tonnes | 25.41 (-10.52) |
24.68 (-11.25) |
- *The amount of credits created through removal by forests is the estimated amount of CO2 removed by the constituent project (annual average).
- Note:
- The results of other Group companies are included with ENEOS.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Targets (Scope 1 + 2)
| FY2025 target | FY2026 target | FY2027 target | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ENEOS Group operational greenhouse gas emissions (Reduction compared to FY2013) |
27.00 million tonnes or less (-7.46 million tonnes) |
26.35 million tonnes or less (-8.11 million tonnes) |
26.81 million tonnes or less (-7.65 million tonnes) |
- Note:
- Base year greenhouse gas emissions (fiscal 2013): 34.46 million tonnes
To reach these targets, we are focusing our efforts in three main areas.
- 1) Curbing operational greenhouse emissions by improving the energy efficiency of our manufacturing and business operations through energy saving, fuel conversion, and the use of renewable energy.
- 2) Using carbon dioxide capture and storage (CCS) for emissions remaining after the above measures are carried out, and storing the captured CO2 underground.
- 3) Any remaining greenhouse gas emissions after the above two measures will be removed through removal by forests and other biogenic CO2 removal methods.
Calculation of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- Targets
The Group’s greenhouse gas emissions reduction targets include not only carbon dioxide (CO2) but also six other greenhouse gases: methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorinated compounds, sulfur hexafluoride, and nitrogen trifluoride. These reduction targets were set with the aim of reducing pure emissions. Furthermore, we did not use the Sectoral Decarbonization Approach (SDA) in setting our targets, as the SBTi is in the process of preparing guidance for the oil and gas sector. - Calculation
The Group calculates its total greenhouse gas emissions in accordance with the Act on Promotion of Global Warming Countermeasures (Global Warming Countermeasures Act). This is because compliance with this Japanese law is mandatory. The calculation results include both direct measurements and estimates. Estimates are made in accordance with the calculation method stipulated in the Global Warming Countermeasures Act. Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas emissions only cover companies subject to consolidated accounting and do not include other business entities.
Major Initiatives
Energy Conservation at Production Sites
The Group’s refineries and plants are pursuing energy conservation through measures such as increasing the number and efficiency of heat exchangers and introducing higher efficiency rotary equipment.
Operational greenhouse gas emissions (Scope 1+2)* in fiscal 2024 totaled 24.68 million tonnes, down from the previous fiscal year due to a decline in domestic demand in addition to improvements in the efficiency of refinery operations.
Meanwhile, our crude oil refining energy consumption intensity worsened by 0.22 points from the previous fiscal year to 9.42 (oil equivalent consumption volume [kL]/crude distillation unit equivalent throughput [thousand kL]) due to a reduction in refinery operations.
In fiscal 2024, the Group invested around 0.85 billion yen in facilities for energy conservation. Going forward, we remain committed to pursuing greater energy conservation by introducing energy-saving technologies and optimizing operations at our refineries.
- *Calculated in accordance with the Act on Promotion of Global Warming Countermeasures, taking into account electricity sold and heat sold.
Initiatives in Research and Development
The Group is moving forward with research in the following fields in order to realize energy transitions.
In fiscal 2024, the ENEOS Group spent a total of around 16.1 billion yen on research and development.
- Technical development for the manufacture, storage, transport, and supply of hydrogen derived from renewable energy sources
- Technical development for the manufacture of synthetic fuels from hydrogen and CO2
- Technical development for the manufacture of hydrogen and the optimization of storage battery operation plans, which contribute to the effective use of renewable energy
- Technical development for biofuels
- Technical development for recycling of plastic resources and used tires
- Rationalization and streamlining of oil refining processes using digital technology, etc.
- Development of fuel-efficient and energy-efficient lubricants and immersion cooling fluids that contribute to the reduction of CO2 emissions
- Exploration of lubricant recycling technologies and development of products using plant-based lubricant base oils
Comprehensive Collaboration Activities with Waseda University
In November 2019, ENEOS concluded an agreement with Waseda University on comprehensive collaboration activities to promote innovation toward achieving a sustainable society. Through comprehensive and multi-disciplinary open innovation, from innovative technology to humanities and social sciences for the social implementation of technology, we are exploring the seeds of innovation that will contribute to the realization of the sustainable society of the future, and also working to develop energy storage technologies and new materials.
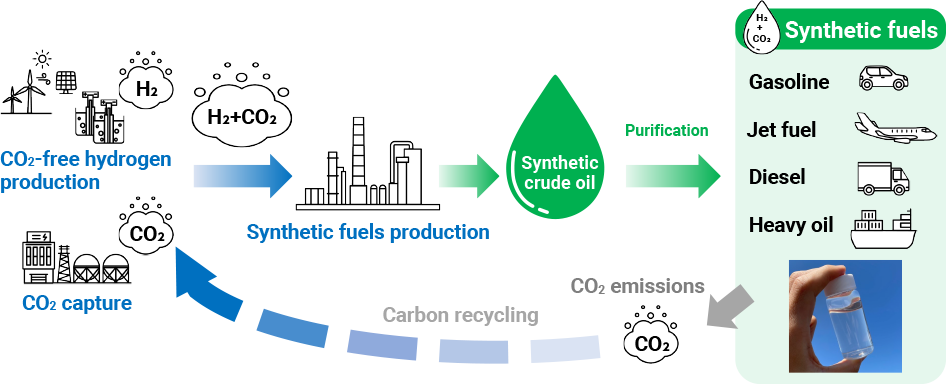
Development of Manufacturing Technologies for Synthetic Fuels Derived from Renewable Energy
ENEOS is working on the development of manufacturing technology for synthetic fuels that can replace fossil fuels such as jet fuel, gasoline, and diesel to achieve carbon neutrality in a wide range of fields, such as aircraft and vehicle mobility and raw materials for chemicals and lubricants.
Synthetic fuels are carbon-neutral fuels produced using hydrogen derived from renewable energy sources and CO2, which means that they can reduce CO2 emissions throughout the product life cycle. In addition, as their properties are equal to those of conventional fossil fuels, these synthetic fuels can be acceptable in existing vehicles, refinery facilities, and distribution routes, meaning they will play a vital role in realizing energy transitions.
In September 2024, we began operations at Japan’s first synthetic fuels demonstration plant that can handle the entire process of producing synthetic fuels from raw materials. The plant is located within the Central Technical Research Laboratory. The synthetic fuels produced there were used to fuel shuttle buses (diesel) and vehicles (gasoline) for guests and related parties at the 2025 Osaka-Kansai Expo.
ENEOS aims to establish manufacturing technologies for synthetic fuels early and their social implementation with the support of the Green Innovation (GI) Fund*, which was adopted in April 2022.
- *A fund administered by the Japanese government that provides support to companies working to address management issues to help reach Japan’s goal for carbon neutrality by 2050. The fund offers ongoing financial assistance over a 10-year period in areas ranging from R&D and demonstration projects to social implementation, covering fields in energy-related industries, including the hydrogen and ammonia fuel industries; transportation and manufacturing-related industries; and household and office-related industries.
Renewable Energy-Based Synthetic Fuels Production Process
Supporting Research on Hydrogen Energy Supply through the ENEOS Hydrogen Trust Fund
ENEOS established the ENEOS Hydrogen Trust Fund in March 2006 in order to help speed up the realization of a hydrogen society.
The fund is Japan’s first public trust specializing in supporting research on the supply of hydrogen energy. The fund is large enough that a stable supply of research grants worth 50 million yen (up to 10 million yen per project) can be provided for around 30 years to support innovative and pioneering basic research into hydrogen energy supply systems. As of June 2025, the fund’s assets total around 600 million yen, which will make it possible to provide stable grants for approximately 10 years going forward.
Developing Manufacturing Technologies for Bioethanol (Cellulosic Ethanol)
In the journey to carbon neutrality, bioethanol is expected to be used in various applications such as automobile fuels and raw materials for chemical products. In recent years, it has also attracted attention as a raw material for sustainable aviation fuel (SAF). On the other hand, the bioethanol produced around the world today comes mainly from food crops such as sugarcane and corn, raising concerns that it may compete with food.
ENEOS is developing technology for producing bioethanol (cellulosic ethanol) using cellulose resources that do not compete with food, such as woody biomass like pulp and used paper, as raw materials. In fiscal 2023, ENEOS concluded a joint development agreement with TOPPAN Holdings Inc., aiming for commercialization through a project combining the preprocessing process developed by TOPPAN Holdings using hard-to-recycle used paper as a raw material and the ethanol continuous production process developed by ENEOS.
In addition, ENEOS Corporation, Suzuki Motor Corporation, Subaru Corporation, Daihatsu Motor Co., Ltd., Toyota Motor Corporation, Toyota Tsusho Corporation, and Mazda Motor Corporation are jointly participating in the Research Association of Biomass Innovation for Next Generation Automobile Fuels to promote research on production technology for bioethanol fuels for automobiles.
Initiatives in Procurement and Logistics
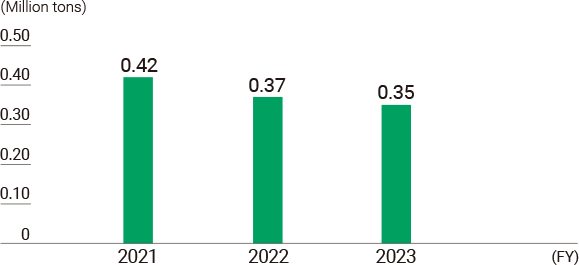
With regard to marine transportation, which primarily involves the transport of crude oil to Japan, ENEOS is making active efforts to use oil tankers with superior delivery efficiency and fuel efficiency, and to improve fuel consumption by optimizing transportation routes and controlling navigation schedules and speeds.
Regarding land transportation, in addition to consolidating oil depots and improving the distribution efficiency of tank trucks, we are working to reduce fuel consumption through efforts such as insisting that drivers turn off their engines when stopped.
CO2 Emissions from Domestic Transport
- Notes:
- Scope: ENEOS
- Domestic transport based on the Act on Rationalizing Use of Energy and Shifting to Non-fossil Energy (Energy Conservation Act)
Distribution Stage Initiatives
ENEOS is actively implementing power-saving measures at its service stations nationwide through efforts such as the installation of solar panels and the adoption of LED lighting.
Consumption Stage Initiatives
The Group’s CO2 emissions from the use of sold products (Scope 3) in fiscal 2024 totaled 159.00 million tonnes.
The ENEOS Group is working to reduce CO2 emissions at the consumption stage through the development and sale of environmentally friendly products, which contribute to a lower environmental impact. We have specified standards and procedures for certification of our environmentally friendly products and services and manage these appropriately.
Main environmentally friendly products
- Fuel-efficient/high-performance multipurpose lubricants
- Specialized fluids for electric vehicles and hybrid vehicles
- Natural gas and LNG
- High-performance cleaning agents
- Liquid crystal polymers
- Electricity generation using renewable energy
Certification of Products That Contribute to Avoided Emissions
In September 2024, ENEOS began certifying environmentally friendly material products that contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions across society as “products that contribute to avoided emissions.”
Regarding the calculation of greenhouse gas emission reduction effects from the use of these products that contribute to avoided emissions, we are constantly updating our internal guidelines to reflect the latest rules being discussed for international standardization. In addition, to confirm the validity of our calculations, we undergo reviews by Mizuho Research & Technologies Co., Ltd., an external expert, in an effort to ensure that our figures are highly reliable.
The total reduction effects are calculated to be 1.86 million tonnes of CO2-e/year in fiscal 2024.
- *For details, see ENEOS’s Environmentally Friendly Products(Available in Japanese only).
Sales of Carbon-Offset Natural Gas and LNG
In fiscal 2021, ENEOS began selling carbon-offset1 natural gas and LNG through the use of CO2 credits2 from overseas forest protection projects, and is supplying these products to utility gas providers.
ENEOS’s carbon-offset natural gas and LNG utilize CO2 credits generated from forest protection projects to reduce greenhouse gas emissions on a global scale. ENEOS is also contributing to the creation of local employment and the protection of biodiversity through these efforts.
- 1The CO2 emitted in the process from extraction to combustion of natural gas is offset to virtually zero.
- 2CO2 credits attested by a highly reliable verification institution for CO2 reduction effects generated by environmental conservation projects.
Working with Business Partners (CSR Procurement)
We implement CSR procurement, in which we take into account social impacts, such as effects on the environment, when purchasing materials and other goods and services.
For details, see Supply Chain Management.
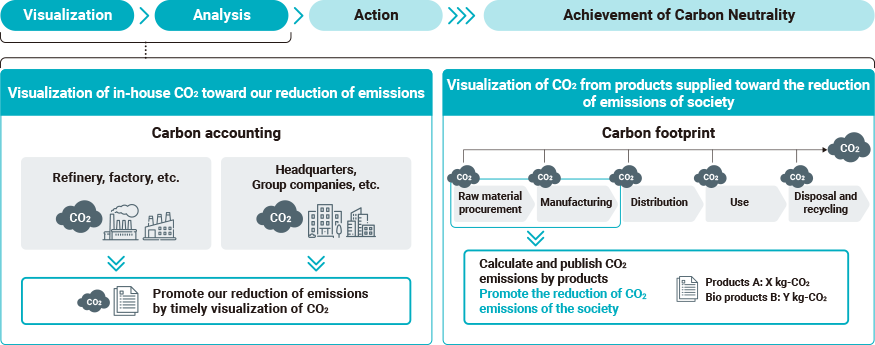
Visualizing CO2 to Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions
We are working toward the visualization of greenhouse gas emissions in order to reduce operational greenhouse gas emissions and downstream greenhouse gas emissions from sold products.
ENEOS established a CO2 visualization system because it is important to determine emissions in a timely manner in order to reduce emissions at its refineries. We established this system to enable centralized management of operational emissions and calculation of emissions (carbon footprint: CFP1) for each product. This is the first CFP calculation in the domestic petroleum industry that uses real data obtained at refineries.
The system will be used to streamline statutory reporting, manage the implementation of plans through monthly forecasting and result management, and provide CFP data to customers. In 2024, we started providing CFP data for some products to customers, and we plan to gradually expand the scope of the applicable products.
The development of this system aims to achieve unified monitoring and management of carbon information on a per-product basis, analyze the impact that decarbonization initiatives in manufacturing has on CFP and visualize CFP at the new product planning stages, and create business opportunities by highlighting the environmental value of low-carbon products.
Our CFP data will be “cradle to gate2,” meaning it will cover all greenhouse gas emissions from raw materials procurement to product shipment. We will use the life cycle assessment (LCA) method3 to calculate emissions associated with material procurement and product manufacturing.
- 1Carbon footprint of products (CFP) is a system for converting greenhouse gas emissions throughout the life cycle of a product or service, from the procurement of raw materials to manufacturing and beyond, to CO2.
- 2Refers to the process from raw materials procurement to production within the life cycle stages, comprising raw materials procurement, manufacturing, distribution, sales, use and maintenance, disposal and recycling.
- 3LCA (life cycle assessment) methodology involves quantitatively evaluating the environmental effects of product manufacturing throughout the entire life cycle, from procurement of raw materials to manufacturing, transport, use, and disposal.
ENEOS Group CO2 Visualization
Businesses Helping to Address Climate Change
Advancement of Renewable Energy Power Generation Business
The Group is working to grow its Renewable Energy business, centered on ENEOS Renewable Energy (ERE), a leader in the development and operation of renewable energy power plants in Japan. The Group’s renewable energy generation capacity stands at 1,375,000 kW (as of June 2025, including facilities under construction).
The renewable energy power plants operated by ERE generated approximately 1.6 billion kWh of electricity in fiscal 2024, which is equivalent to the annual electricity consumption of approximately 400,000 average households. This contributed to a reduction in CO2 emissions of approximately 670,000 t-CO2 compared to conventional power generation methods.
Going forward, by combining ERE’s advanced business development and power plant operation capabilities with the Group’s long-standing expertise in the energy business, we will further develop and speed up the business to become Japan’s leading supplier of renewable energy and contribute to the realization of the 3E+S (energy security, economical efficiency and environment, plus safety) of energy in a decarbonized society. For information on our renewable energy power plants, see the ERE website.



Planned Power Generation Projects
| Power generation project | Generation capacity* | Planned start of operation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Japan | Kudamatsu Fourth Mega Solar Power Plant | 17 MW | November 2025 |
| Chita Mega Solar Power Plant | 22 MW | April 2026 | |
| JRE Sakata Wind Farm (replace) | 21 MW | February 2027 | |
| Chugoku-Shikoku Region High-Voltage Bulk Solar Power Plant No. 1 | 48 MW | December 2027 |
- *100% of generation capacity
Generation Capacity by Energy Source (As of June 30, 2025)
| Thermal1 (10 sites) |
Oil, etc. (7 sites) |
917 MW |
| LNG (CCGT2) (3 sites) | 1,389 MW | |
| Solar (99 sites) | 952 MW | |
| Wind (13 sites) | 187 MW | |
| Biomass (2 sites) | 91 MW | |
| Total | 3,537 MW | |
- 1Thermal capacity does not include refinery in-house power generation.
- 2Gas-fired thermal power plant with combined cycle gas turbines (CCGT)
- Note:
- Hydro power will be excluded from the calculations from fiscal 2025 onward.
Renewable Energy Power Generation (Fiscal 2024)
| Solar | 1,236,616 MWh |
| Hydro | 23,865 MWh |
| Wind | 472,228 MWh |
| Biomass | 566,882 MWh |
| Total | 2,299,591 MWh |
The greenhouse gas emission factor* for ENEOS Power in fiscal 2024 was 0.000508 t-CO2/kWh (after adjustment; provisional figure).
- *Greenhouse gas emission factor (after adjustment) for regular service offerings (excluding renewable energy/renewable energy [FIT] services and CO2-free electricity services).
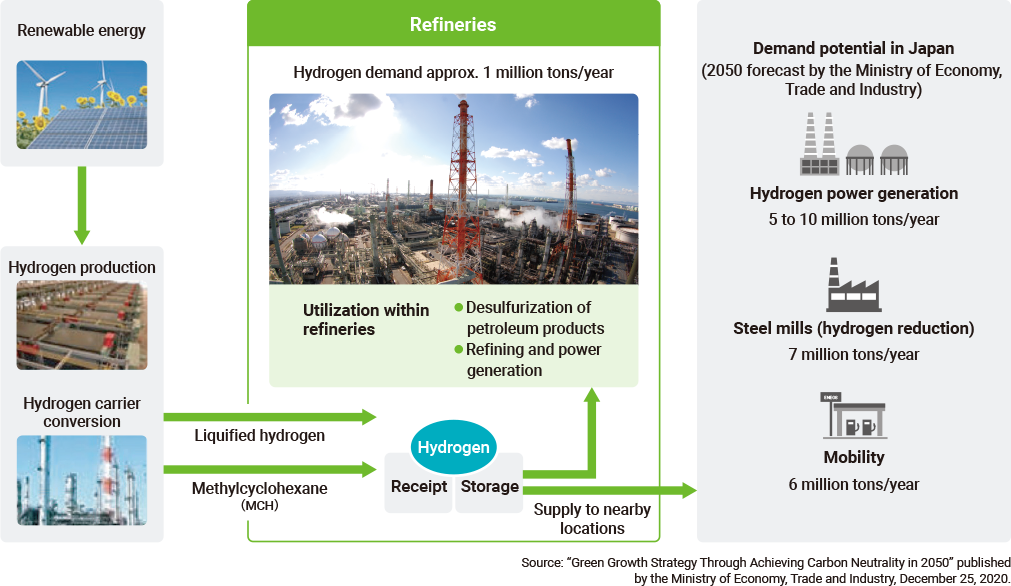
Establishment of a Hydrogen Supply Chain


Hydrogen has the potential to contribute to decarbonization in a wide range of economic activities in transportation, industry, and other sectors. We see hydrogen as one of the promising next-generation energy sources that holds the key to achieving carbon neutrality.
First, in the transportation sector, there are around 8,900 fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) (as of June 30, 2025), and approximately 150 hydrogen stations located nationwide in Japan. ENEOS operates 33 of these facilities (as of June 30, 2025). The growth of FCVs as commercial vehicles, such as buses and trucks, in addition to passenger vehicles, is expected due to factors such as their short hydrogen refueling time and long driving range. The Japanese government has prioritized support for commercial vehicles in its Basic Hydrogen Strategy, which was revised in 2023, and ENEOS is also considering the development of hydrogen stations in line with this strategy. Additionally, with an eye toward carbon neutrality, we are also introducing some hydrogen stations that produce and sell hydrogen using electricity derived from renewable energy sources and water electrolysis equipment.
Furthermore, ENEOS is implementing a number of collaborative projects with local governments and leading companies in Japan and overseas for the establishment of a supply chain for transporting and supplying Japan with hydrogen produced overseas, where there is abundant renewable energy and other resources. As part of this effort, we are focusing on methylcyclohexane (MCH), a hydrogen carrier, in order to transport green hydrogen from overseas to Japan in large quantities and with high efficiency. We are now working on the development of our proprietary Direct MCH® technology, which contributes to cost reduction (see the news release for details).
ENEOS refineries have the potential to serve as hubs for the stable supply of hydrogen because, in addition to the fact that they already have expertise in safely handling large quantities of hydrogen and can utilize existing infrastructure, such as ports, piers and tanks, they are located near large-scale business sites, such as power plants and steel mills. We will fully utilize these advantages in our exploration of the development of a hydrogen supply chain.
Building a Hydrogen Supply Chain Using Our Refineries as Hubs
Initiatives for the Development of a Hydrogen Supply Chain
Overseas
| Project/Organization | Region | Overview |
|---|---|---|
| Development of a Japan-Australia hydrogen supply chain | Australia | We are studying collaboration in Australia on the potential for the low-cost, stable supply of hydrogen produced from renewable energy. The project will study more efficient production of methylcyclohexane (MCH) and maritime transport of MCH to Japan as a form of hydrogen storage and transport. |
| Development of a hydrogen supply chain (derived from renewable energy) in Malaysia | Malaysia | The project will manufacture several tens of thousands of tonnes of hydrogen in Sarawak, Malaysia, using electricity derived from renewable energy generated at a hydroelectric power plant. Thereafter, the hydrogen will be converted to MCH and transported by chemical tanker to demand centers outside Malaysia. For more information, see the news release. |
| Equity participation for building a hydrogen supply chain between Japan and the U.S. | United States | In order to verify the commercial feasibility of manufacturing cost-competitive clean hydrogen in the Gulf of Mexico and exporting MCH to Japan, we made an equity investment in MVCE Gulf Coast, LLC, a U.S. company. For more information, see the news release. |
Japan
| Project (Location) | Overview |
|---|---|
| Selection for NEDO Green Innovation Fund | The following four demonstration projects were selected by the National Research and Development Agency, New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) for its Green Innovation Fund (Available in Japanese only): (1) large-scale demonstration of an MCH supply chain; (2) direct MCH electrosynthesis (Direct MCH®) technology development; (3) hydrogen single fueled power generation equipment demonstration; and (4) demonstration project for the commercialization of a liquefied hydrogen supply chain. The demonstration project period is planned to last until the end of fiscal 2030. For more information, see the following news releases. ・News release on demonstration projects (1) to (4) ・Joint news release with Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd. and Iwatani Corporation on demonstration project (4) (Available in Japanese only) |
| Development of hydrogen stations | There are around 155 hydrogen stations in Japan, 31 of which are operated by ENEOS (as of September 30, 2025). ENEOS participates in the Japan Hydrogen Station Network Joint Company (Japan H2 Mobility, abbreviation: JHyM), which was established in February 2018 by automobile manufacturers, infrastructure companies, and financial investors. Through collaboration in this all-Japan consortium, ENEOS is working on the strategic development and efficient operation of hydrogen stations. ENEOS Hydrogen Stations(Available in Japanese only) For more information, see the news release (Available in Japanese only). |
| Commercial sales of hydrogen derived from renewable energy produced at hydrogen stations (First in Japan) | The project will market hydrogen produced by water electrolysis using electricity generated from solar panels installed at hydrogen stations and renewable-energy-derived electricity procured from the ENEOS Group. The project has introduced a hydrogen energy management system (EMS) for optimal control of water electrolysis unit operations based on the amount of renewable energy electricity generated and hydrogen demand. Going forward, the project will aim for the manufacture of hydrogen using low-cost electricity by collaborating with virtual power plants (VPP), which remotely control hydrogen EMS and various energy resources. Next-Generation Energy Supply Platform(Available in Japanese only) For more information, see the news release (Available in Japanese only). |
| Hydrogen utilization study at Haneda Airport and surrounding areas | We will investigate the hydrogen supply potential using a model where hydrogen produced overseas is imported to the Kawasaki coastal area and then transported to the vicinity of Haneda Airport, which is a demand area. We will also investigate the hydrogen demand potential by utilizing hydrogen for electricity, heat, and GSE vehicles in Haneda Airport facilities, and hydrogen utilization in the surrounding area. For more information, see the news release. |
| Study for the development of a large-scale green hydrogen supply chain in Hokkaido | In February 2024, we exchanged a memorandum of understanding for a study on the establishment of Japan’s largest green hydrogen supply chain with Idemitsu Kosan Co., Ltd. and Hokkaido Electric Power Co., Inc. By around 2030, we aim to build a water electrolysis plant (100 MW or more) in the western Tomakomai area of Hokkaido, which will be the largest in Japan, capable of producing more than 10,000 tonnes of green hydrogen annually. In turn, we aim to build a supply chain that supplies the produced green hydrogen to local factories and other facilities by pipeline. For more information, see the news release. |
| Collaborative study for utilization of hydrogen at the Mizushima Industrial Complex | ENEOS will study the receipt, storage, and supply of hydrogen at the Mizushima Refinery, aiming to supply the hydrogen needed for fuel use in the test furnace and steel mill at JFE Steel Corporation’s West Japan Works (Kurashiki District). For more information, see the news release. |
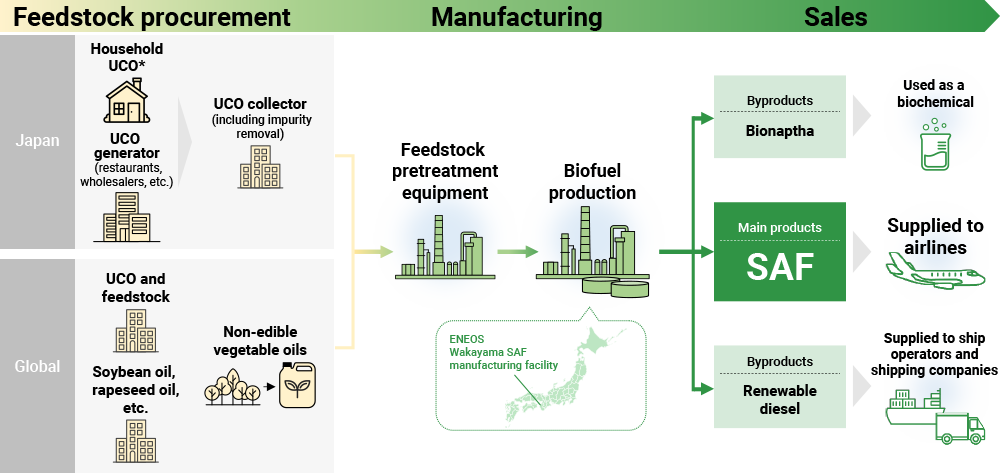
Building an SAF Supply Chain
ENEOS is working to build an SAF* supply chain by establishing an in-house SAF manufacturing system and an import system.
For the in-house manufacturing system, we are currently proceeding with plans to install SAF manufacturing equipment that utilizes used cooking oil (hereinafter referred to as UCO) and tallow as feedstocks at our Wakayama Plant, with the aim of establishing a mass production and supply system with an annual capacity of 400,000 KL from fiscal 2028 onward. Globally, in July 2025 we agreed to enter the biofuel manufacturing and sales business in the United States with Par Pacific Holdings, Inc. and Mitsubishi Corporation. By utilizing and partially renovating existing facilities at the Kapolei Refinery in Hawaii, operated by Par Pacific, we will expect to produce approximately 150,000 KL of SAF per year.
On the import system, we signed agreements for the purchase and sale of SAF with Japan Airlines Co., Ltd. (JAL) in July 2024 and Skymark Airlines Inc. in February 2025. As the first domestic oil company to import SAF into Japan, we are positioned to supply the aviation industry, which is pursuing SAF procurement both domestically and internationally. Through these partnerships, we aim to accelerate SAF adoption and growth in Japan.
Regarding feedstock, currently 120,000t of UCO from restaurants and other businesses (total 500,000t per year) is exported overseas, while approximately 90% of the UCO generated by ordinary households (total 100,000t per year) is discarded. In order to utilize this UCO as SAF feedstock, we are considering establishing a collection and recycling scheme through partnerships with other companies.
For more details of our initiatives, see Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAF).
- *Sustainable aviation fuel: Low-carbon, sustainable aviation fuel made from feedstocks such as UCO, biomass, and waste residues.
Building an SAF Supply Chain
Launched Sales of Environmental Attributes
ENEOS began selling environmental attributes (EA)1 of SAF to corporate aircraft users in September 2024. These EAs are sold on a platform certified by a third party to ensure their traceability.
ENEOS aims to provide a stable supply of energy, including the supply of SAF to the aviation industry. However, cost and supply chain constraints have made it difficult for aviation industry stakeholders to promote the use of SAF. Through this initiative, ENEOS will establish a mechanism to share the costs and benefits of SAF with aviation industry stakeholders and support the aviation industry and its corporate customers in achieving their goals of net-zero CO2 emissions (see the news release for details).
In addition to selling SAF EAs, ENEOS has also purchased SAF EAs for its own operations, insetting2 137.504 t-CO2 related to employee business travel by air.
- 1Greenhouse gas emissions reduction effects associated with the use of SAF. Airlines will reduce direct CO2 emissions from aircraft operations (Scope 1 for airlines). At the same time, indirect CO2 emissions from air cargo transport, employee business trips, etc. (Scope 3 for airline users) will be reduced.
- 2Carbon insetting refers to reducing emissions within the scope of a company’s business activities. For example, CO2 emissions from air travel during business trips can be reduced by utilizing SAF EAs. This differs from carbon offsetting, which offsets emissions outside of business activities, as insetting focuses on reductions within business operations.
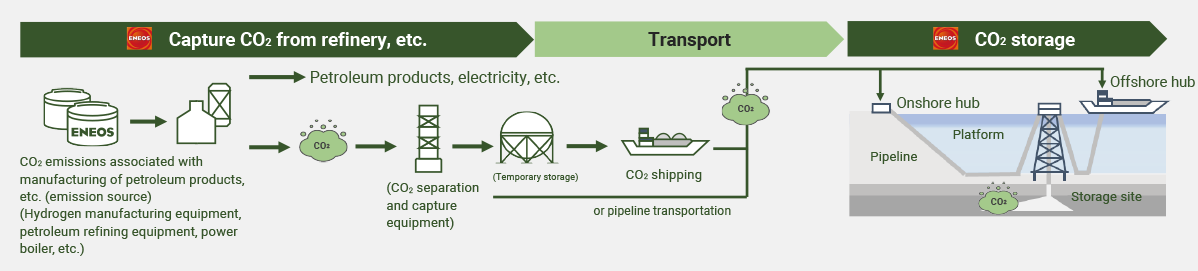
CCS Business
The Group is preparing to launch a large-scale CCS business in the early 2030s in cooperation with the government, which aims to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050, and various businesses that are actively working to achieve that goal.
In the Group’s oil and natural gas E&P business, we commercialized a CCS/CCUS business in 2016 in Texas, USA, in which CO2 captured from exhaust gas at a thermal power plant is injected underground. Therefore, we already have the necessary technology and knowledge for geological evaluation and CO2 injection. While maximizing this expertise, we will collaborate with other companies to scale up operations and minimize costs, aiming for the full-scale implementation of CCS.
Activities in the CCS Business
| Start | Operating companies | Activity details |
|---|---|---|
| February 2023 | ENEOS, ENEOS Xplora | West Japan Carbon dioxide Storage Survey Co., Ltd. established jointly by three companies, Electric Power Development Co., Ltd. (J-POWER), ENEOS, and ENEOS Xplora, for the storage of CO2 in western Japan |
| March 2023 | ENEOS Xplora | Acquisition of shares of Japan Drilling Co., Ltd., which has offshore drilling technology necessary for CO2 storage |
| August 2023 | ENEOS、ENEOS Xplora | Selected along with J-POWER as a contractor for the Japan Organization for Metals and Energy Security (JOGMEC)’s fiscal 2023 “Study on the Implementation of Japan’s Advanced CCS Project” |
| December 2023 | ENEOS、ENEOS Xplora | Started joint study with Santos Limited for the establishment of a CCS value chain between Japan and Australia |
| March 2024 | ENEOS Xplora | Started joint study with Chevron New Energies for the establishment of a CCS value chain |
| March 2024 | ENEOS、ENEOS Xplora | Mitsubishi Corporation, PETRONAS CCS Solutions, ENEOS and ENEOS Xplora concluded a memorandum of understanding for a study on the establishment of an overseas CCS value chain for CO2 emissions from Tokyo Bay |
| September 2024 | ENEOS、ENEOS Xplora | Our project off the coast of northern Peninsular Malaysia was selected by the Japan Organization for Metals and Energy Security (JOGMEC)’s fiscal 2024 “Engineering Design Work for Japanese Advanced CCS Projects” |
| October 2024 | ENEOS、ENEOS Xplora | Our project off the coast of western Kyushu was selected by the Japan Organization for Metals and Energy Security (JOGMEC)’s fiscal 2024 “Engineering Design Work for Japanese Advanced CCS Projects” |
Domestic CCS Value Chain of ENEOS
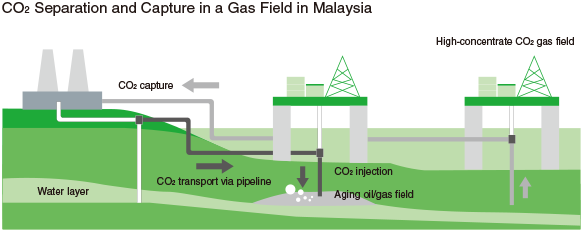
Oil and Gas E&P Using CO2-EOR and CCS Technologies
ENEOS Xplora carries out its business activities with attention to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
The company is taking part in a project in the state of Texas in the United States to increase output from a depleted oil field by injecting CO2 captured from the flue gas of a thermal power plant. Since April 2017, a total of 5.00 million tonnes of CO2 has been captured and injected into the oil field for storage through this project, greatly contributing to increasing oil output and lowering greenhouse gas emissions using CO2-EOR (enhanced oil recovery) technology.
In March 2024, ENEOS Xplora signed a contract with Malaysia's state-owned oil company PETRONAS and PETRONAS Carigali Sdn. Bhd., a wholly-owned subsidiary of PETRONAS, for the production of five undeveloped gas fields containing high concentrations of CO2 off the coast of Peninsular Malaysia, and also signed a joint operation agreement with PETRONAS Carigali. This is a combination of conventional development and CCS, in which CO2 captured from gas fields is injected underground, with the aim of developing low-carbon oil and natural gas.

Forest Absorption (Enhancement of Biogenic CO2 Removals)
The Group utilizes biogenic removals from forests and other sources as an important means of removing CO2. In order to achieve a 73% reduction in operational emissions by fiscal 2040 and carbon neutrality by fiscal 2050, we are implementing initiatives to create and utilize forest-derived carbon credits in Japan and overseas.
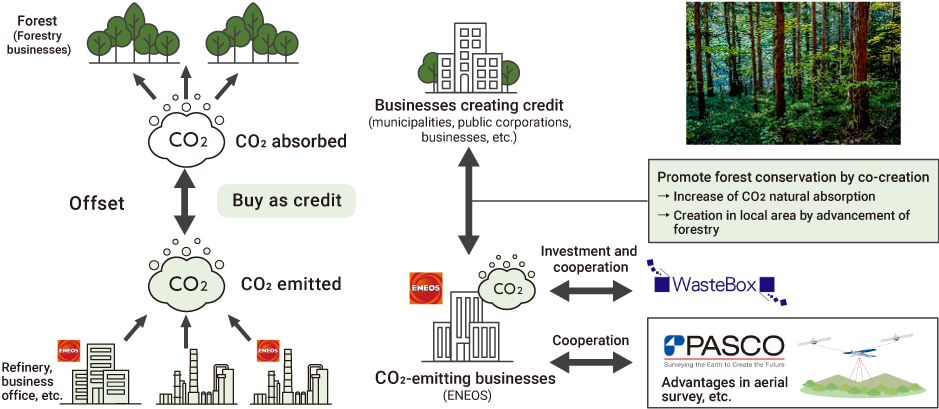
Projects for Removal by Forests
| Region | Start | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Japan | January 2022 | Signed a partnership agreement with Kumakogen Town, Ehime Prefecture for the creation of J-Credits* |
| November 2022 | Signed a partnership agreement with Niigata Public Corporation of Agriculture and Forestry for the creation of J-Credits | |
| November 2023 | Signed a partnership agreement with Mori Town, Hokkaido, in collaboration with Nippon Life Insurance Company for the creation of J-Credits | |
| June 2024 | Signed a partnership agreement with Wakayama Public Corporation for Forests and Greenery for the creation of J-Credits | |
| November 2024 | Signed a partnership agreement with Fukushima Midorino Morizukurikosha Public Interest Incorporated Association for the creation of J-Credits | |
| December 2024 | Signed a partnership agreement with JForest Tsurui Village in Hokkaido and The Norinchukin Bank for the creation of J-Credits | |
| May 2025 | Signed a partnership agreement with Ichinoseki City, Iwate Prefecture for the creation of J-Credits | |
| August 2025 | Signed a partnership agreement with Shimane Prefecture, Shimane Forest Association (J Forest), Shimane Forest Association, and Shimane Forestry Corporation for the creation of J-Credits | |
| Overseas | July 2023 | Invested in Eastwood Climate Smart Forestry Fund I, a US forestry fund formed by the Sumitomo Forestry Group |
- *A system in which the Japanese government certifies the amount of CO2 and other greenhouse gas emissions reduced through the introduction of energy-saving equipment and the use of renewable energy, as well as the amount of CO2 and other greenhouse gases absorbed through appropriate forest management, as “credits”