Basic Approach
As a corporate group responsible for the stable supply of energy and materials, the ENEOS Group believes that ensuring safe operations is the basis of our business survival and social credibility, as well as the source of our competitive edge.
Based on this understanding, safety has been prioritized in the Group Philosophy, and our basic policy on safety and security has been stipulated in the Group Code of Conduct.
Based on the above, each Group company has established its own safety policy in accordance with its business characteristics and assesses risks pertaining to occupational safety, thereby ensuring multiple layers of effective safety activities. Specifically, we aim to enhance our safety activities and safety training programs, in which the employees of our contractor companies also participate, and we have established preventive and emergency measures to cope with all manner of accidents, problems and natural disasters.
We check with our labor unions to make sure efforts are being made to maintain the facilities needed to ensure the health and safety of labor union members (Article 90 of the Ancillary Agreement to the Labor Agreement).
ENEOS Group Code of Conduct (excerpt)
- 2.Safety and security
- (1)We regard safety and security as the foundation of our business activities, set high safety and security standards, always ensure safety and security, and take appropriate measures to prevent any incidents and injuries.
- (2)We have established preventive and emergency measures to minimize damage to our business sites caused by natural disasters, including earthquakes. We also make every effort to protect the lives and safety of our directors, officers and employees, communities, and others concerned.
- (3)We shall not work under the influence of alcohol or drugs, when ill, or under other conditions where safety cannot be ensured.
ENEOS Group Safety Policies
Each ENEOS Group company has established a policy on occupational health and safety which states its commitment to prioritizing and fully ensuring the safety of its workers.
- ENEOS, ENEOS Materials, ENEOS Power
We aim to ensure that nobody gets hurt and to eliminate accidents. - ENEOS Xplora
Ensuring that Health, Safety and Environment (HSE) considerations are given prevailing status over our other business considerations. - ENEOS Renewable Energy
We prioritize the safety of our officers and employees, contractors and their staff, and local residents.
See the following for further details on the safety policies of the Group’s principal operating companies.
Structure
For information about our structure, see ESG Management Structure.
We have established the ENEOS Group Safety, Health & Environment Council, chaired by the officer responsible for the Safety, Health & Environment Department at ENEOS Holdings. The council meets, in principle, twice annually, to share information on the status of occupational injuries and the implementation of safety activities at the Company and its principal operating companies, as well as to discuss and develop measures to prevent occupational injuries.
Operation of Safety Management Systems and Status of Certification
Each Group company has built safety management systems tailored to its respective business characteristics. Our companies are continuously making efforts to raise safety awareness and prevent occupational injuries through means such as implementing regular safety education and training, conducting investigations into the causes of incidents and formulating and implementing measures to prevent recurrence.
ENEOS has established and implemented its own safe operations management system (SOMS), which conforms to ISO standards, at all of its refineries and plants.
ENEOS Renewable Energy has newly introduced and is operating an SOMS at onshore wind power plants and biomass power plants.
ENEOS Xplora has established and is operating a health, safety and environment (HSE) management system, which conforms to ISO and other standards.
ENEOS Materials has built a risk-based safety management system and is operating a flexible and effective safety management structure tailored to the risk characteristics of each site.
JX Advanced Metals is moving ahead with the acquisition of ISO 450011 and JIS Q 451002 certification, and by March 2025, 13 domestic business sites had obtained certification. The remaining business sites, including those that have newly joined the JX Advanced Metals Group, plan to acquire certification in fiscal 2025 and beyond.
- 1An international standard for occupational health and safety management systems
- 2JIS standard based on the international standard ISO 45001, with additional requirements particular to Japan
Material Issues, Plans and Results
Fiscal 2024 Targets, Results and Progress
Evaluation: Achieved/Steady progress Not achieved
| Material ESG Issue | Initiative | Target (KPI) | Results/Progress | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ensuring safety / Health enhancement | Reduction in occupational injuries | Serious occupational injuries*: zero * Occupational fatalities |
1 | |
| TRIR*: 1.0 or less * Number of occupational injuries per one million work hours (non-lost-time occupational injuries + lost-time occupational injuries and fatalities) |
|
2.24 (Total of employees and employees of contractor companies) | ||
| LTIR*: 0.0 for employees, 0.3 or less for employees of contractor companies * Number of lost-time occupational injuries and fatalities per one million work hours |
|
0.67 for employees, 0.90 for employees of contractor companies |
||
Results of Major Initiatives for Ensuring Safety
The Group prioritizes and is fully committed to ensuring the safety of its workers at all times. We have set material targets for zero serious occupational injuries (occupational fatalities), TRIR1 of 1.0 or less and LTIR2 of 0.3 or less for fiscal 2030, and we implement comprehensive safety activities and safety training for all employees, including those of contractor companies.
However, the TRIR for fiscal 2024 was 2.243, and the LTIR was 0.763, both falling short of the targets. There was also one major accident in fiscal 2024 and one in fiscal 2025, both at ENEOS refineries. The company takes the occurrence of serious occupational injuries in two consecutive years very seriously and the president has issued messages on safety to all employees. We will conduct a thorough examination of the causes of these accidents, put measures in place to prevent recurrence, and roll out these measures at other refineries to prevent similar accidents from occurring.
- 1Total recordable incident rate (TRIR): Number of occupational injuries per one million work hours (non-lost-time occupational injuries + lost-time occupational injuries and fatalities)
- 2Lost time incident rate (LTIR): Number of lost-time occupational injuries and fatalities per one million work hours
- 3Total of employees and employees of contractor companies
Accident Report
Occupational Injury at Negishi Refinery (Fatal Accident)
In August 2024, there was a fatal workplace accident in which an employee of a contractor company was caught between construction materials and a materials storage rack while transporting construction materials in preparation for scheduled maintenance.
Measures to Prevent Recurrence
- We will establish appropriate maintenance and management procedures for construction material storage areas, and make any necessary improvements to construction material storage facilities.
- Our employees and employees of contractor companies will work together to improve awareness of safety throughout our worksites and will engage in activities to ensure that this awareness is maintained.
Gas Leak at the Sakai Refinery (Fatal Accident)
In May 2025, a leak of gas containing hydrogen sulfide occurred during preparations for scheduled maintenance. Three workers involved in this task were taken to hospital by ambulance. One of the workers, an ENEOS employee, died, and the two other workers, employees of contractor companies, were hospitalized.
Measures to Prevent Recurrence
We have established an accident investigation committee that includes outside experts. When an accident report reflecting the findings of the committee regarding the cause of the accident and recommendations for measures to prevent recurrence is released, it will be distributed internally and actions will be taken to prevent recurrence.
- For information about , see the Editorial Policy.
Occupational Injuries
(Persons)
| FY2022 | FY2023 | FY2024 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of occupational injuries | Directly hired employees | Fatalities | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Lost work time | 12 | 19 | 45 | ||
| Subtotal | 12 | 19 | 45 | ||
| Contractors (contractor companies, etc.) | Fatalities | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| Lost work time | 17 | 21 | 41 | ||
| Subtotal | 17 | 21 | 42 | ||
| Total | 29 | 40 | 87 | ||
- Notes:
- Scope of occupational injury statistics: Changed in fiscal 2024. ENEOS Holdings, ENEOS, ENEOS Xplora, ENEOS Materials, ENEOS Power, ENEOS Renewable Energy, JX Advanced Metals, and their group companies.
Fiscal 2023 and before: ENEOS Holdings, ENEOS, ENEOS Xplora, JX Advanced Metals, and their group companies (excluding ENEOS sales and distribution group companies).
Occupational Injury Frequency Rate*
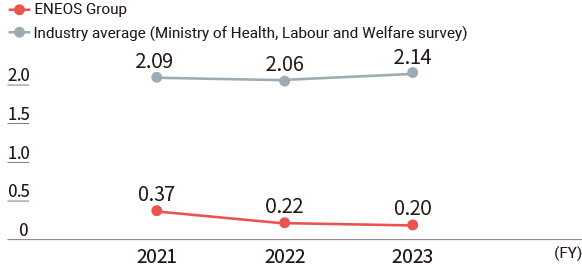
- Notes:
- Scope of data: Changed in fiscal 2024. Refineries, plants, and business sites of ENEOS, ENEOS Xplora, ENEOS Materials, ENEOS Power, ENEOS Renewable Energy, and JX Advanced Metals.
Fiscal 2023 and before: Refineries, plants, and business sites of ENEOS, ENEOS Xplora, and JX Advanced Metals.
(For details, see Data.) - * Frequency rate: The number of injuries and fatalities per million cumulative hours worked; indicates the frequency of occurrence of occupational injuries.
Definition of terms by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare(Available in Japanese only)
Occupational Injury Severity Rate*
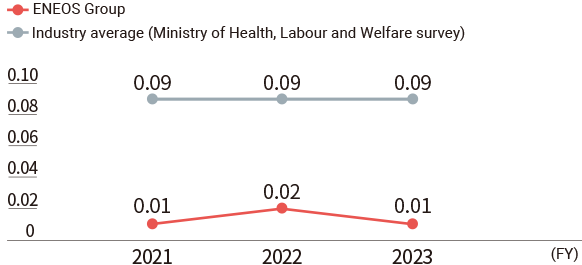
- Notes:
- Scope of data: Changed in fiscal 2024. Refineries, plants, and business sites of ENEOS, ENEOS Xplora, ENEOS Materials, ENEOS Power, ENEOS Renewable Energy, and JX Advanced Metals.
Fiscal 2023 and before: Refineries, plants, and business sites of ENEOS, ENEOS Xplora, and JX Advanced Metals.
(For details, see Data.) - * Severity rate: The aggregated number of work days lost per thousand cumulative hours worked; indicates the severity of occupational injuries.
Definition of terms by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (Available in Japanese only)
TRIR and LTIR
(Persons)
| Item | FY2022 | FY2023 | FY2024 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total recordable incident rate (TRIR) | Directly hired employees | 1.00 | 0.94 | 1.92 |
| Contractors (contractor companies, etc.) | 2.59 | 2.45 | 2.71 | |
| Total | 1.87 | 1.77 | 2.24 | |
| Lost time injury rate (LTIR) | Directly hired employees | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.67 |
| Contractors (contractor companies, etc.) | 0.51 | 0.45 | 0.90 | |
| Total | 0.37 | 0.31 | 0.76 |
- Notes:
- Scope of data: Expanded in fiscal 2024. Employees and employees of contractor companies of ENEOS Holdings, ENEOS, ENEOS Xplora, ENEOS Materials, ENEOS Power, ENEOS Renewable Energy, JX Advanced Metals, and their Group companies.
- Fiscal 2023 and before: Employees of ENEOS Holdings, ENEOS head office and 11 refineries and plants, ENEOS Xplora head office and four business sites, and JX Advanced Metals head office and five business sites.
(For details, see Data.) - TRIR: Number of occupational injuries per one million work hours (non-lost-time occupational injuries + lost-time occupational injuries and fatalities), excluding heat stroke (first aid)
LTIR: Number of lost-time occupational injuries and fatalities per one million work hours
Major Initiatives
Increased Scope of Data for TRIR and LTIR
As part of the management of safety-related targets, the principal operating companies use TRIR and LTIR as indicators. In fiscal 2022, we decided to expand the scope of data for TRIR and LTIR.
Up to fiscal 2023, the scope of data covered employees and employees of contractor companies at business sites under the direct control of the principal operating companies. From fiscal 2024, the expanded scope of data also covers the group companies of each of the principal operating companies.
Safety Activities
Group companies are working to raise safety awareness and enhance safety management.
Every year in July, ENEOS and ENEOS Power release video messages on safety by their presidents to all employees, demonstrating the companies’ commitment to safety. At its refineries and plants, ENEOS has implemented a behavior-based safety (BBS) system that is used to facilitate safe operations by focusing on individual behavior.
As part of its safety activities, ENEOS Xplora encourages all employees to appropriately exercise their stop work authority (SWA) whenever there are unsafe conditions or actions at the worksite, allowing anyone to temporarily halt work as necessary.
At ENEOS Materials, we systematically provide classification-leveled and job-specific training tailored to employees, ranging from new hires to highly experienced workers. In particular, at our business sites, we offer opportunities to learn specifically about the risks of accidents such as falls, getting fingers caught, and being entangled in machinery, in an effort to enhance hazard awareness.
At ENEOS Power, we utilize work-related accident cases and safety education materials shared by the company to enhance safety awareness at power plants. We also implement various initiatives such as safety patrols involving our investee companies.
At ENEOS Renewable Energy, we plan and carry out training for all employees to experience hazards firsthand in order to raise safety awareness. Employees working at power plants identify hazards through risk assessments and implement responses. Additionally, for contractor companies and their employees, we check the safety activities that should be performed before starting work and provide warnings, and we also regularly monitor the status of these safety activities thereafter.
At JX Advanced Metals, we analyze the factors behind occupational accidents and work to create an environment where unsafe behavior does not occur and is not allowed. Additionally, to enhance safety awareness and hazard sensitivity, we provide training to improve workplace patrol abilities, primarily for managers, and conduct training to improve foremen’s skills at each business site. We continue to develop key frontline personnel, while also creating basic educational materials on hazard prediction and 5S, to improve the safety knowledge of each individual worker.
Group-wide Safety Action Items
In order to prevent serious occupational injuries, we designated preventing falls, separating people from heavy machinery, and preventing heatstroke as the three safety action items for the principal operating companies. We established these action items in the ENEOS Group guidelines in February 2020.
Since fiscal 2021, we have reflected the three safety action items, positioned as common issues for the principal operating companies, into the safety activities of each company. The principal operating companies are also sharing safety initiatives with their own group companies as part of their efforts to eliminate occupational injuries.
Group-wide Safety Action Items
- Preventing falls
- Separating people from heavy machinery
- Preventing heatstroke
Hazard Simulation Training
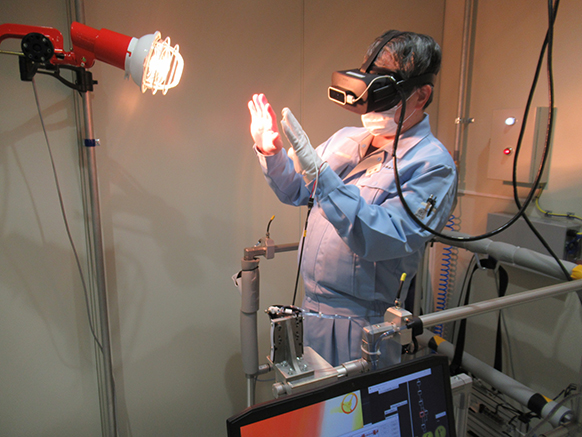
The Group launched the ENEOS Group Safety Education Center in Hitachi City, Ibaraki Prefecture in 2013 to enable workers to learn about the hazards inherent in day-to-day operations through simulated experiences. Since fiscal 2017, the center has implemented a training program unique to the Group using virtual reality (VR) technology.
The program enables workers to feel what it is like to be involved in an accident and think about victims’ psychological state, as well as accident causes and preventive measures.
VR makes it possible to simulate accidents that cannot be safely replicated in the real world, such as steam explosions, being struck by heavy machinery, getting caught in rotating equipment, and falling from heights.
In fiscal 2024, 1,162 persons participated in training at the facility, bringing the total number since the establishment of the center to 15,470.
In addition, ENEOS, ENEOS Materials, and JX Advanced Metals have also installed hazard simulation training equipment at their major production sites.
Workers at these sites, including those from contractor companies, are required to undergo training using this hazard simulation training equipment before engaging in onsite work. With these and other efforts, we are working to ensure safety across the entire Group.
Using AI to Ensure Safety While Walking
In fiscal 2022, ENEOS introduced an AI-driven system for analyzing walking motion as a way to improve movement safety. The system uses a special device to measure a person’s walking speed, stride length, center of gravity, and other elements to determine the level of safety in the walking motion. The system then uses the results to provide suggestions for exercises or other ways to improve safety while walking.
In fiscal 2023, we added one of these systems to enable analysis of more people.
Improving Human Skills
As human factors are a major cause of occupational accidents and injuries, we have focused for many years on training to arm employees with the knowledge and technical skills needed to implement procedures and rules without fail. In recent years, however, there is growing awareness in the manufacturing industry, referencing leading initiatives in the healthcare and airline industries, about the importance of stepping up initiatives to improve non-technical skills, including status confirmation of work environments and communication among workers, in addition to compliance with procedures and rules. Accordingly, we are incorporating knowledge and activities for the improvement of these non-technical skills.
Foundation for Safe and Stable Operations
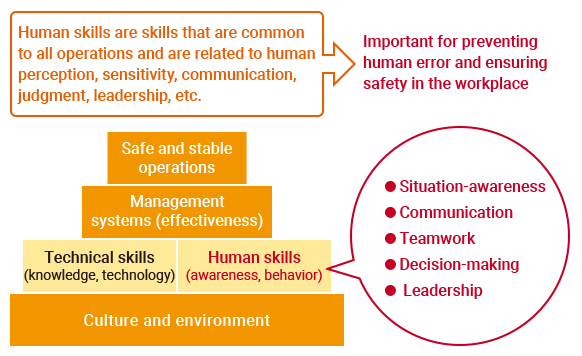
In the ENEOS manufacturing division, we refer to these non-technical skills as human skills, which we have stipulated in the activity guidelines for improving human skills in the manufacturing division. In accordance with these guidelines, at all of our plants and refineries, top management shares the importance of human skills, and systems have been put into place for the implementation of various forms of education and training and the integration of the resulting skills into existing daily safety activities in the workplace. In this manner, we are working to improve the human skills of all employees in the manufacturing division to prevent human-factor-related accidents and occupational injuries.
Initiatives with Contractor Companies
At ENEOS refineries and other facilities, we provide training for all contractor company employees that are new to our worksites on site safety rules and share information about onsite facilities. When selecting contractor companies, in addition to evaluating the safety management aspects of work execution, we conduct regular evaluations of the status of their safety management after the start of the business relationship, identify areas for improvement and follow up on the implementation status.
Moreover, in order to ensure proper safety management of contractor companies, we require the primary contractor to submit and execute a safety management plan, establish KPIs for the contractor company, conduct regular monitoring and evaluations, and report on improvements.
Main Initiatives at Refineries and Plants for Earthquakes
The Group implements various earthquake measures at its refineries and plants.
Measures to Protect Lives

As a precaution against earthquakes and tsunamis, we have voluntarily implemented seismic reinforcement of our onsite offices and production unit control rooms, with priority given to the protection of human life.
We have also designated locations and methods for evacuation in case of an earthquake or tsunami, and we carry out disaster preparedness drills every year.
Measures for Seismic Reinforcement of Facilities

We are carrying out legally required seismic reinforcement work for tanks that store hazardous materials.
Upgrade work on floating-roof tanks subject to this requirement was completed before the statutory deadline. As for internal floating-roof tanks, which became subject to legislation in fiscal 2011, we completed seismic reinforcement work by the statutory deadline (end of fiscal 2023).
For high-pressure gas facilities, we have already completed seismic assessments following government instructions, as well as the retrofitting of spherical tanks with braces to increase earthquake resistance, taking into account the effects of the Great East Japan Earthquake. Seismic countermeasures for facilities of high importance were completed in fiscal 2021, marking the completion of our seismic reinforcement of high-pressure gas facilities.
Measures to Mitigate Damage from Disasters
We have installed seismographs at all of our refineries and plants as part of a system that automatically shuts down equipment in a prompt and safe manner in the event of an earthquake, depending on the intensity.
Countermeasures against Accidents and Malfunctions
Disaster Prevention Facilities

At our refineries, plants, and stockpiling terminals, we have established self-defensive organizations for disaster prevention and installed necessary disaster response equipment and facilities in preparation for potential accidents and disasters. We have also established a defensive organization for cooperative disaster prevention with nearby companies to improve the disaster preparedness of industrial complexes.
Oil Spill Countermeasures

We have multiple oil dikes surrounding our storage tanks and systems to prevent leakage from spreading offsite. In addition, to promptly respond to oil spills at sea, we have oil fences to prevent oil spills from spreading and oil recovery vessels in place.
Fire Countermeasures

We have equipped our refineries and plants with fire extinguishing equipment, such as large chemical firefighting vehicles, high-altitude chemical water cannon vehicles, and high-capacity foam water cannon systems, for response in the event of a major fire.
Our facilities also have disaster response vessels with firefighting capabilities to respond to fires at sea.
Disaster Drills

We regularly implement comprehensive disaster response drills for our self-defensive organizations for disaster prevention to ensure that we can respond in a quick and agile manner should an actual disaster occur. We also hold other drills, including joint disaster preparedness drills involving local fire departments as well as disaster response organizations from nearby companies and local communities.
Ensuring a Stable Supply
The Group has established a backup system for ensuring a stable supply in the event of a major disaster that impacts the functions of production and shipping sites through collaboration with other production and shipping sites. We also conduct drills and training regularly to ensure that our sites can continue to function in the event of a disaster.