The 3Rs (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle)
Basic Approach
The ENEOS Group is doing its part to develop a recycling-oriented society by reducing waste in its own activities as well as in society. We are promoting resource conservation, along with waste reduction, reuse, and recycling within the Group, while strengthening circular economy initiatives throughout our entire supply chain.
Structure
For information on our structure, see Environmental Management.
Material Issues, Plans and Results
Fiscal 2024 Targets, Results and Progress
Evaluation: Achieved/Steady progress Not achieved
| Material ESG Issue | Initiative | Target (KPI) | Results/Progress | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contribution to the development of a recycling-oriented society | Reduction in landfill disposal | Waste-to-landfill ratio: Maintain zero emissions (less than 1%) | 0.8% | |
Results
- For information about , see the Editorial Policy.
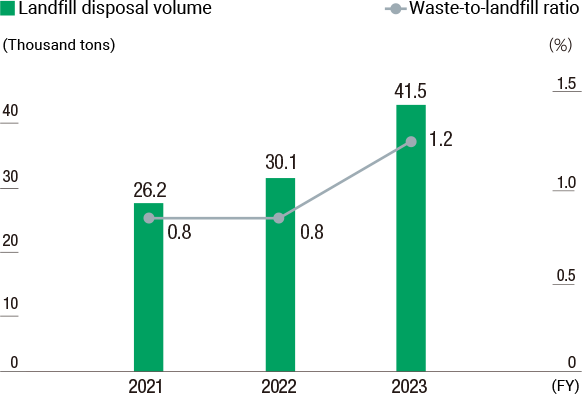
Landfill Disposal Volume and Waste-to-Landfill Ratio
- Note:
- For detailed data, see Data.
Major Initiatives
Waste Reduction
The Group manages and recycles waste appropriately, with a target of maintaining zero emissions (waste-to-landfill ratio of less than 1%).
In fiscal 2024, waste totaled 3,749 thousand tonnes and landfill waste totaled 28 thousand tonnes. The waste-to-landfill ratio was 0.8%, indicating that we achieved our zero-emissions target. Factors contributing to the change from the previous fiscal year include a decrease in landfill waste generated during pavement repair work and building demolition work, which resulted in a decrease in the landfill disposal volume and waste-to-landfill ratio.
Sludge is the most common waste generated by refineries and plants, accounting for about 40% of the total waste volume. We pursue recycling and reuse through initiatives for waste reduction, including using the collected particulate matter and sludge released from oil refineries as raw materials for cement, and the repeated use of neutralized sludge1 at our smelting and refining facilities. In addition, we use LCA methodology2 in evaluating the development of certain lubricant products.
- 1Material generated by the neutralization reaction in the smelting process.
- 2LCA methodology involves quantitatively evaluating the environmental effects of product manufacturing throughout the entire life cycle, from procurement of raw materials to manufacturing, transport, use, and disposal. LCA is an acronym for “life cycle assessment.”
Targets and Processes Surpassing Legal Requirements for Industrial Waste
In response to Keidanren’s (Japan Business Federation) call for the development of a recycling-oriented society, oil companies have been working on waste reduction and recycling at their refineries. The target for the petroleum industry in Keidanren’s Voluntary Action Plan for Establishing a Sound Material-Cycle Society is to maintain a waste-to-landfill ratio of 1% or less in fiscal 2025. ENEOS is striving to reduce the waste-to-landfill ratio by setting a target for its refineries to maintain “zero emission plus” (waste-to-landfill ratio of less than 0.3%), which is more rigorous than the Keidanren target.
Responsible Management of Waste
We confirm whether waste emitted at our refineries is disposed of responsibly in accordance with our duty under the Waste Disposal and Public Cleansing Act. Each of our refineries systematically conducts audits of waste disposal contractors.
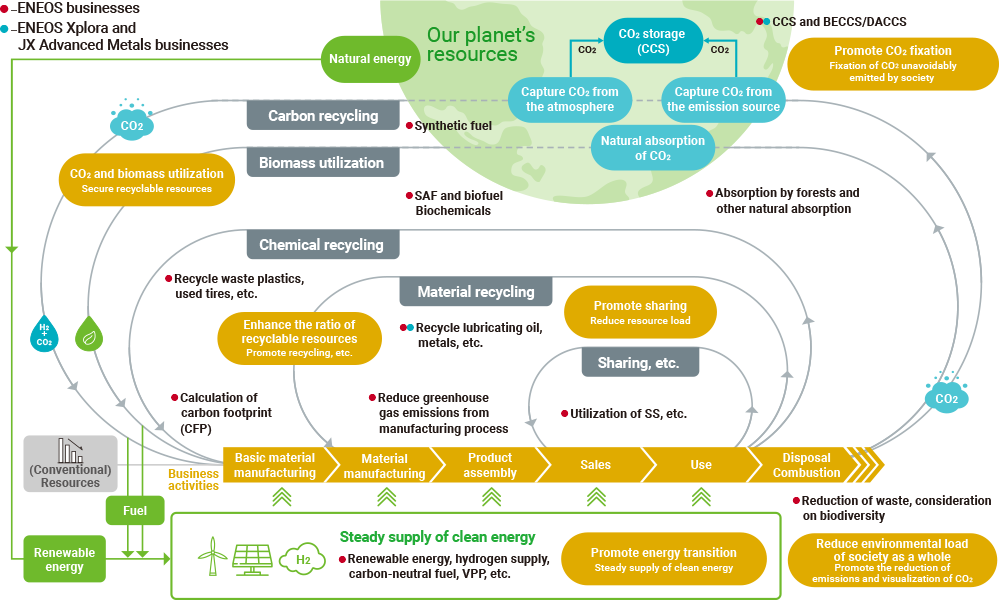
Pursuit of a Circular Economy
The Group is promoting a circular economy1.
Society is shifting from a linear economy2 to a circular economy—from a mass production, mass consumption economy to an economy that recycles and reuses resources. A circular economy goes one step further than the 3Rs by considering the environment from the design stage, using maintenance to lengthen product life, and enhancing usage efficiency by incorporating leasing and sharing.
The Group has established three action guidelines for realizing a circulating society: namely, protecting finite resources, reducing environmental impact, and leveraging changes in society as opportunities. Under these guidelines, we will supply products that utilize recycled resources and provide materials and services that contribute to resource conservation. We will also reduce CO2 emissions throughout the supply chain by utilizing waste and providing the clean energy needed for resource recycling. We will leverage changes in society, such as changes in consumer behavior and the value placed on environmental contributions, as opportunities to promote a circular economy, thereby contributing to the realization of a carbon-neutral, circulating society.
- 1An economic system that seeks to recycle resources through their effective use in each stage of the value chain
- 2An economic system where products flow in a single direction with resources being consumed and disposed without recycling or reuse
ENEOS Group’s Action Guidelines for Realizing a Circulating Society
Protecting finite resources
Responding to the growing demand for the development of materials that do not rely on conventional resources and for resource efficiency
Reducing environmental impact
Promoting collaboration with the government and society to
utilize waste effectively and reduce CO2 emissions throughout the entire supply chain
Leveraging changes in society as opportunities
Providing products, services, and value that address social needs arising from
changes in consumer behavior and certifying the value to environmental contributions
Circular Economy Initiatives for Realizing a Circulating Society Not Dependent on Conventional Resources
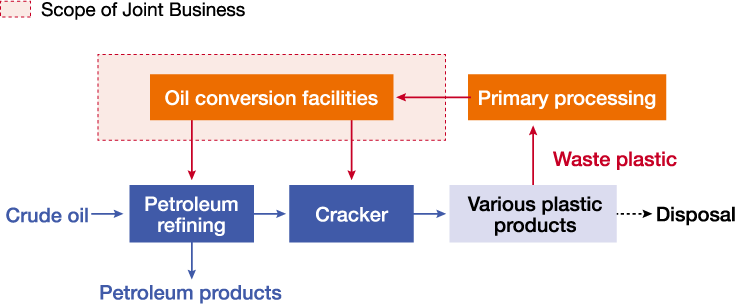
Joint Plastic-to-Oil Conversion Business (Chemical Recycling)
ENEOS is engaged in a joint plastic-to-oil conversion business with Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation at the Kashima industrial complex, site of the Kashima Refinery. In July 2025, the two companies completed construction of a commercial chemical recycling facility with an annual processing capacity of 20,000 tonnes, which will be the largest-scale in Japan on a commercial basis. The recovered oil produced at the facility will be used as a raw material at both companies’ petroleum refinery and naphtha cracker to produce recycled petroleum and plastic products.
Workflow of Plastic-to-Oil Conversion
Recycling Synthetic Rubber from Used Tires (Chemical Recycling)
Synthetic rubber derived from petroleum is one of the main materials used when producing tires. ENEOS, in cooperation with Bridgestone Corporation, aims to establish chemical recycling technology to produce chemicals and other raw materials for synthetic rubber from cracked oil obtained from the precise pyrolysis of used tires. Looking to the future, ENEOS is committed to further improving resource recycling and reducing CO2 emissions in the value chain of the tire/rubber and petroleum/petrochemical industries. In February 2022, this initiative was adopted as a Green Innovation Fund Project of the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO), a national research and development agency.
Asphalt Pavement Utilizing Waste Plastics (Material Recycling)
A typical asphalt pavement is composed of about 95% (by weight) of stones and sand called aggregates, and asphalt, called a binder, holds these aggregates together.
ENEOS is working on the development of asphalt paving technology that replaces all aggregates with waste plastic. Demonstration tests are now underway at the SOYORA Hamamatsu Nishiiba store opened by AEON RETAIL Co., Ltd. in Hamamatsu City, Shizuoka Prefecture in October 2023, and at the ENEOS Platform opened in Ushiku City, Ibaraki Prefecture in March 2024.
Through the use of waste plastics, which are difficult to use in material recycling and are mainly used for thermal recycling, our new asphalt pavement is expected to reduce CO2 emissions by about 40% compared to conventional ones.
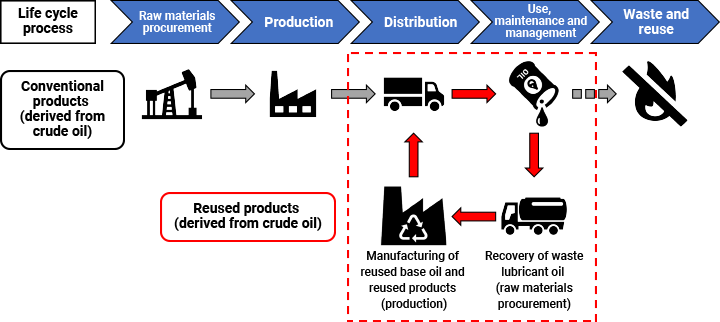
Refining Base Oil from Used Lubricants (Material Recycling)
ENEOS is working to commercialize a resource-circulation process to refine base oil from used lubricants. By recovering and refining base oil—the primary component of lubricant products—from used lubricants, we aim to reduce CO2 emissions throughout the lubricant lifecycle and ensure a stable supply of base oil.
This initiative was selected as part of the Ministry of the Environment’s publicly funded project, Demonstration Project for Building Resource Circulation Systems for Plastics and Other Materials to Support a Decarbonized Society. Through a two-year demonstration project which began in fiscal 2022, we successfully produced low-carbon base oil.
In the technical validation phase, we used engine oil collected from the market as the raw material, with the cooperation of Toyota Motor Corporation.
Scope of Base Oil Refine Business in the Lubricant Life Cycle
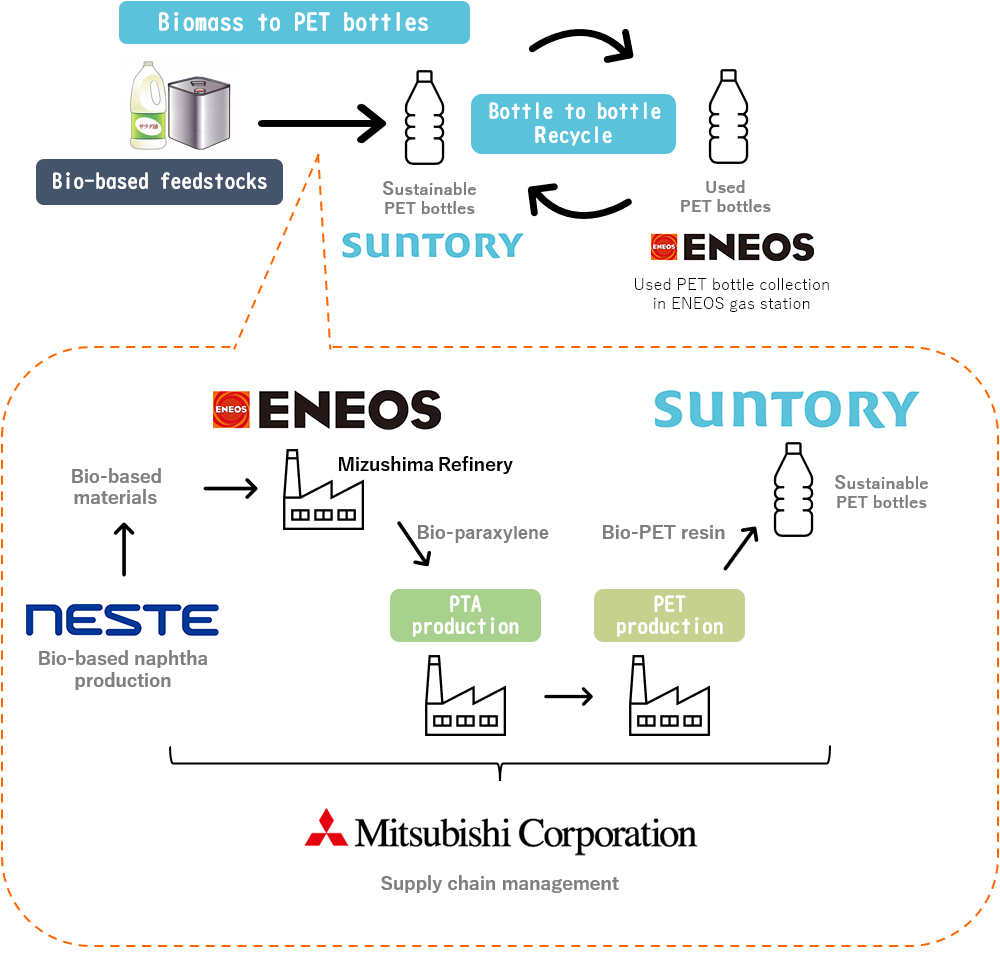
The World’s First Initiative for Bio-Paraxylene Origin “Biomass to PET Bottles” (Effective Utilization of Biomass)
In August 2023, ENEOS reached an agreement with Suntory Holdings Limited and Mitsubishi Corporation to establish a supply chain for sustainable PET resin made from bio-paraxylene. ENEOS manufactures paraxylene, a raw material for PET bottles, and has been studying the possibility of supplying chemicals made from non-fossil raw materials. In the recently established supply chain, bio-paraxylene was produced for the first time in the world on a commercial scale from biomass feedstock made from untapped resources such as used cooking oil, using the mass balance method*, at the ENEOS Mizushima Refinery. PET bottles made using this bio-paraxylene were introduced for some Suntory products in November 2024.
By realizing “biomass to PET bottles” through the use of bio-paraxylene, we will increase the non-fossil resource ratio of petrochemical feedstocks, as indicated in our Carbon Neutrality Plan.
- *A method in which raw materials with specific characteristics, such as biomass raw materials, are mixed with non-biomass raw materials in the distribution and processing process from raw materials to finished products, and those characteristics are assigned to a portion of the product in proportion to the input of raw materials with those characteristics. A system that connects the value of the characteristics of raw materials to the final product by managing the balance of In and Out for each company in the supply chain.
“Biomass to PET Bottles” Supply Chain
Initiative for the Commercialization of Tires Made from Plant-based Synthetic Rubber (Biomass Utilization)
ENEOS Materials is working with Bridgestone Corporation and JGC Holdings Corporation to strengthen collaboration toward commercializing tires made from plant-based synthetic rubber in the early 2030s. This initiative is expected to improve the sustainability of raw materials for tires and contribute to ensuring a stable supply of butadiene in the future.
In July 2024, the Biomanufacturing Ecosystem Construction Project Using Wood and Other Under-Utilized Resources, in which ENEOS Materials and JGC Holdings Corporation are participating, was selected for the Research and Development of Technologies to Promote Biomanufacturing of the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO), a national research and development agency.
Collaboration Among the Three Companies and Division of Roles

Development of Carbon-Neutral Engine Oil (Biomass Utilization)
In December 2024, ENEOS successfully developed an engine oil that helps achieve carbon neutrality. The newly developed engine oil uses 100% plant-derived base oil and is certified to meet API SP1 and ILSAC GF-62 standards, with a viscosity grade of 0W-20.To further advance carbon neutrality, we plan to develop engine oils that comply with the latest specifications—API SQ, ILSAC GF-7, and JASO GLV-23.
- 1API SP: Gasoline engine oil standard set by the American Petroleum Institute
- 2ILSAC GF-6: Gasoline engine oil standard set by the International Lubricant Standardization and Approval Committee
- 3JASO GLV-2: The latest standard set by the Japanese Automotive Standards Organization, offering even greater fuel efficiency than ILSAC GF-7 and guaranteeing industry-leading performance
Battery Recycling Through Sharing Services
ENEOS service stations are working to recycle batteries. In 2022, we established Gachaco, Inc.*, which provides battery sharing services for electric motorcycles. Gachaco has established battery exchange sites at around 50 ENEOS service stations, mainly in Tokyo and Osaka, and is working to build a system for the recycling of batteries.
- *A joint venture of ENEOS Holdings, Honda Motor Co., Ltd., Kawasaki Motors, Ltd., Suzuki Motor Corporation, and Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd.